Australia's National Greenhouse Accounts provide greenhouse gas emission estimates for the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), and for tracking Australia's progress towards its internationally agreed target of limiting emissions to 108% of 1990 levels over the period 0012Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activitiesIn 19, CO 2 accounted for about 80 percent of all US greenhouse gas emissions from human activities Carbon dioxide is naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the Earth's carbon cycle (the natural circulation of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and animals)Ozone is also a greenhouse gas, but it differs from other greenhouse gases in several ways The effects of ozone depend on its altitude, or where the gas is located vertically in the atmosphere Most ozone naturally exists in the layer of the atmosphere called the stratosphere, which ranges from approximately 6 to 30 miles above the Earth's
Ghg Emissions Environmental Reporting
Greenhouse gasses graph
Greenhouse gasses graph-If I were to graph Mykelti's height from now until she graduates high school, a bar graph would provide the most appropriate representation False Biology is the study of The greenhouse effect may increase on Earth because Increasing carbon dioxide will trap more heat Deforestation decreases the levels of CO2 gas in the atmosphereThe planet's average surface temperature has risen about 212 degrees Fahrenheit (118 degrees Celsius) since the late 19th century, a change driven largely by increased carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere and other human activities 4 Most of the warming occurred in the past 40 years, with the seven most recent years being the warmest The years 16 and are tied for




Cause And Effect For Global Warming Time For Change
The greenhouse gas emissions graph for different means of transportation consists of seven line time series graphs with their metric tons of greenhouse gasesTo prevent severe climate change we need to rapidly reduce global greenhouse gas emissions The world emits around 50 billion tonnes of greenhouse gases each year measured in carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 eq) 1 To figure out how we can most effectively reduce emissions and what emissions can and can't be eliminated with current technologies, we need to firstData can be displayed for individual Parties or groups of Parties, for different greenhouse gases or for their sum, and in varying degrees of detail To find the exact GHG data required, the user is advised to consult the following table where typical user requirements are mapped against the data availability on this site
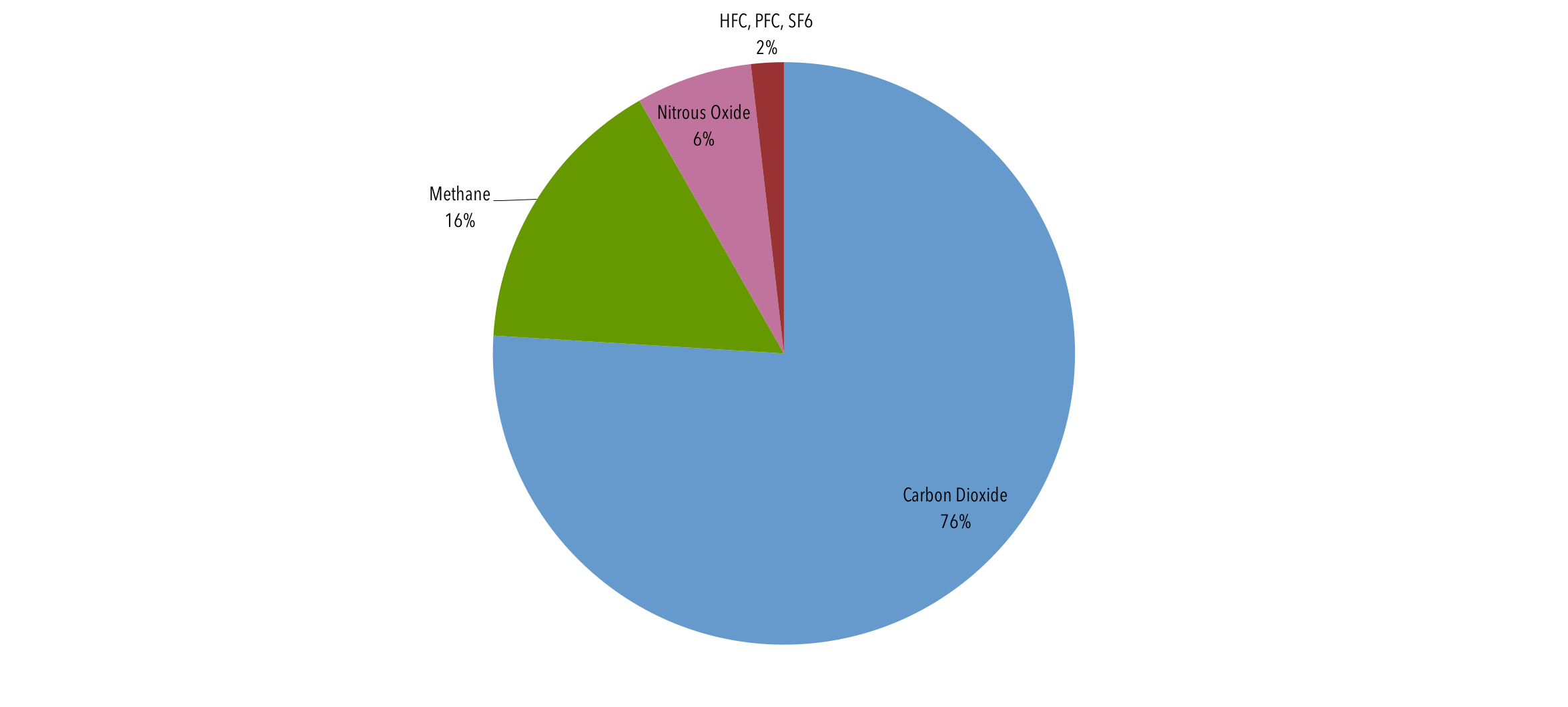
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is an important heattrapping (greenhouse) gas, which is released through human activities such as deforestation and burning fossil fuels, as well as natural processes such as respiration and volcanic eruptionsThe first graph shows atmospheric CO 2 levels measured at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii, in recent years, with average seasonal cycle The graphs show monthly mean carbon dioxide measured at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii The carbon dioxide data on Mauna Loa constitute the longest record of direct measurements of CO 2 in the atmosphere They were started by C David Keeling of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography in March of 1958 at a facility of the National Oceanic andFigure 1 US Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Gas, 1990–19 This figure shows emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and several fluorinated gases in the United States from 1990 to 19 For consistency, emissions are expressed in
CO2 and other longlived greenhouse gases are the volume dial on the climate, and the water vapor amplifies the warming that they produce Texas A&M's Andrew Dessler's work on the importance ofGreenhouse gas emissions from homes and businesses vary from year to year often correlated with seasonal fluctuations in energy use caused primarily by weather conditions Total residential and commercial greenhouse gas emissions, including direct and indirect emissions, in 19 have increased by 3 percent since 1990 Notes Globally, the primary sources of greenhouse gas emissions are electricity and heat (31%), agriculture (11%), transportation (15%), forestry (6%) and manufacturing (12%) Energy production of all types accounts for 72 percent of all emissions




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




This Graph Shows The Increase In Greenhouse Gas Ghg Concentrations In Download Scientific Diagram
Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs livedThe graph to the right shows which activities produce the most greenhouse gases in the United States These greenhouse gases don't just stay in one place after they're added toHuman emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases – are a primary driver of climate change – and present one of the world's most pressing challenges 1 This link between global temperatures and greenhouse gas concentrations – especially CO 2 – has been true throughout Earth's history 2 To set the scene, let's look at how the planet has warmed



File Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector Png Wikipedia



Q Tbn And9gcsimfsyj60oua Uftpgvsarwymidvt7ecxl6tvpe7ykgmq3qnx8 Usqp Cau
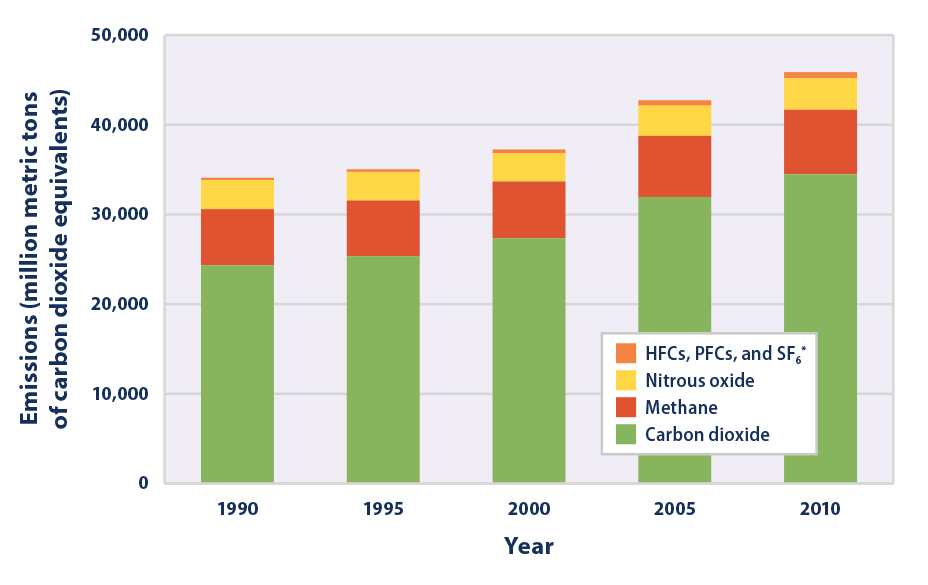
This chart shows the change in global greenhouse gas emissions over time Greenhouse gases are measured in 'carbon dioxideequivalents' (CO 2 e) Today, we collectively emit around 50 billion tonnes of CO 2 e each year This is more than 40% higher than emissions in 1990, which were around 35 billion tonnesFluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) Fluorinated gases are emitted in smaller quantities than the other greenhouse gases, but what they lack in volume they can make up in potency and long lifespans in the atmosphere, ranging from 1270 years for HFCs to ,000 years for PFCs and about 3,0 years for SF6 The food eaten graph is a frequency bar graph showing the average greenhouse gas impact for 50 grams of protein The food wasted graph is a relative frequency bar graph showing the percentage of



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa



Graph Of The Day Noaa Annual Greenhouse Gas Index 1700 18 Desdemona Despair
Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmth The big trick of a greenhouse is that it doesn't let that warmth escape That's exactly how greenhouse gases act They let Levels of the two most important anthropogenic greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide and methane, continued their unrelenting rise in despite the economic slowdown caused by the coronavirus pandemic response, NOAA announced today The global surface average for carbon dioxide (CO2), calculated from measurements collected at NOAA's remote sampling This week we discuss the emissions sources in the United States As defined by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), US greenhouse gas emissions sources can be broken down into five sectors




Cause And Effect For Global Warming Time For Change




Saskatchewan S New Climate Change Strategy Reckless Endangerment Darrin Qualman
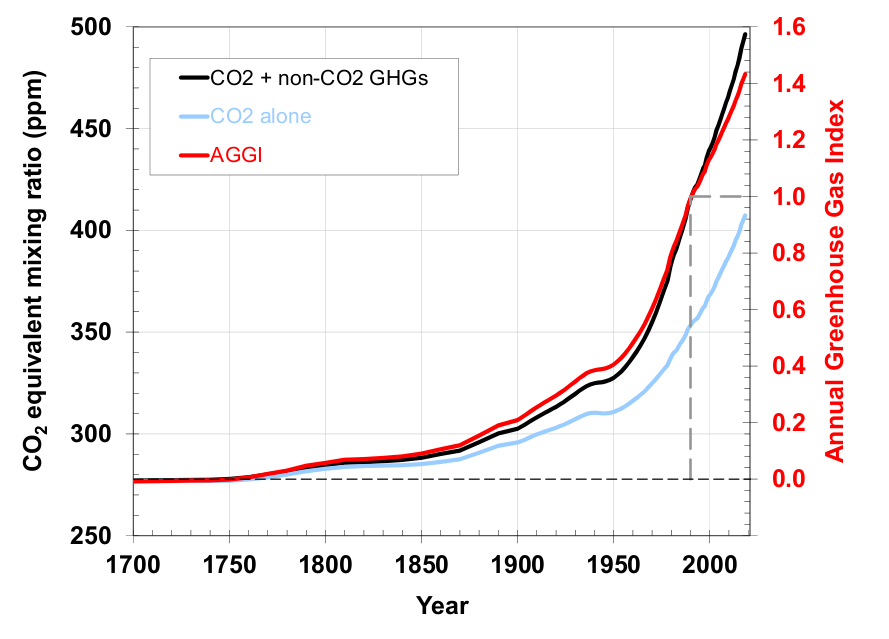
This graph shows the heating imbalance in watts per square meter relative to the year 1750 caused by all major humanproduced greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons 11 and 12, and a group of 15 other minor contributorsGreenhouse gas emissions are greenhouse gases vented to the Earth's atmosphere because of humans the greenhouse effect of their 50 billion tons a year causes climate changeMost is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels coal, oil, and natural gas The largest polluters include coal in China and large oil and gas companies, many stateowned by OPEC and Russia The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming
Direct and WelltoWheel Emissions Vehicle emissions can be divided into two general categories air pollutants, which contribute to smog, haze, and health problems; Explore this interactive graph Click and drag to display different parts of the graph To squeeze or stretch the graph in either direction, hold your Shift key down, then click and drag The graph shows the average of a set of temperature simulations for the th century (black line), followed by projected temperatures for the 21st century based on a range of emissions scenariosGreenhouse Gas Emissions from Animal Agriculture Greenhouse gases (GHGs) absorb infrared radiation and cause the greenhouse effect, which warms the Earth1 GHGs are both natural gases, such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and nitrous oxide, as well as humanmade gases, including chloro and hydrofluorocarbons2
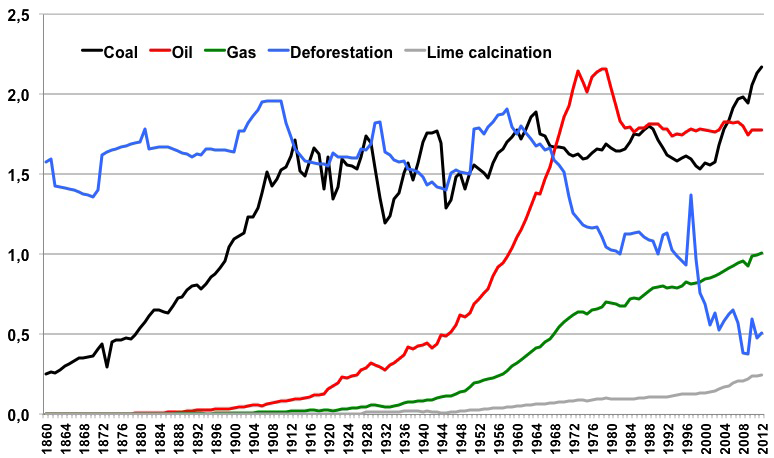



How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici
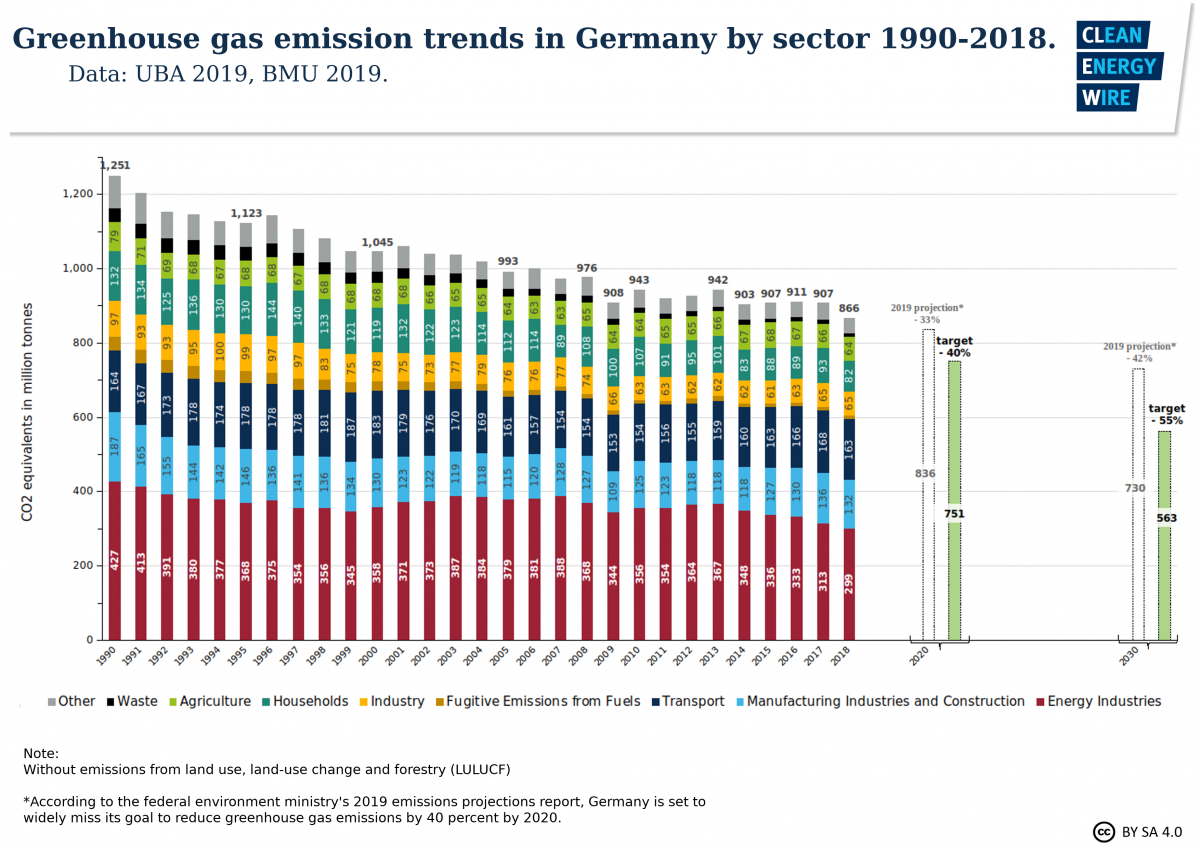



Germany Sees Largest Emissions Drop Since 09 Recession Clean Energy Wire
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data The Oregon Global Warming Commission submits a report to the Oregon Legislature every two years, publishing data on current greenhouse gas emissions, trends, and steps we need to take to reduce emissions The data below is taken from the 18 Oregon Global Warming Commission report"Dumping greenhouse gases into the atmosphere makes the atmosphere more humid And since water vapor is itself a greenhouse gas, the increase in humidity amplifies the warming from carbon dioxide" Specifically, the team found that if Earth warms 18 degrees Fahrenheit, the associated increase in water vapor will trap an extra 2 Watts ofGeneral The Interactive Data Visualization tool gives users a way to explore the abundance of different gases at more than 0 sampling sites around the world You can view graphs showing how the amount of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, and various chlorofluorocarbons have changed over time at any NOAA sampling site
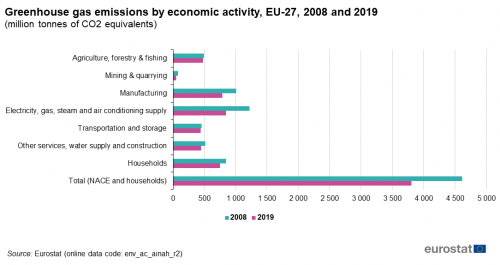



Greenhouse Gas Emission Statistics Air Emissions Accounts Statistics Explained




Assessment Of The Trends Of Greenhouse Gas Emission In Ethiopia Engdaw Geography Environment Sustainability
But CO 2 is not the only greenhouse gas Others, including methane and nitrous oxide, have also had a significant impact on global warming to date The first interactive chart shows per capita greenhouse gas emissions This is measured as the sum of all greenhouse gases, and given by a metric called 'carbon dioxide equivalents'And greenhouse gases (GHGs), such as carbon dioxide and methaneDonovan Harshbarger is an independent artist creating amazing designs for great products such as tshirts, stickers, posters, and phone cases



Chart How Ambitious Is The Uk S Emissions Target Statista




A Graph Of Per Capita Income Versus The Per Capita Greenhouse Gas Download Scientific Diagram
Graphic A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect En la gráfica se comparan los cambios en la temperatura de la superficie global (línea roja) y la energía del Sol que recibe la Tierra (línea amarilla) en vatios (unidades de energía) por metro cuadrado desde 10 New Zealand's greenhouse gas emissions is a direct measure of the 'Human activities generating greenhouse gases' topic Stats NZ and the Ministry for the Environment must report on topics related to the five environmental domains air, atmosphere and climate, fresh water, land, and marine You can visit other EPA pages to learn more about EPA's national inventory and how it relates to EPA's Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program To view a graph, you can either pick from the full list in the Index of Charts or create a graph by choosing options from the five dropdown menus below Some dropdown menu options are unavailable and may be




Greenhouse Gas Emissions




Community Greenhouse Gas Emissions




What Are Carbon Emissions And Why Do They Matter Earthhero Blog




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Set To Rise Fast In 21 The Economist




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Surge To New Record World Meteorological Organization




Global Warming Potential Of Land Use Related Greenhouse Gas Emissions Download Scientific Diagram



Graph Of The Day Antropocene Atmospheric Experiment Ghg Climate Forcing Increased 29 Over Years Bits Of Science



Effects Greenhouse Effect



c News Special Reports Greenhouse Gas Emissions Rising



1




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Colorado Major New Greenhouse Gas Report Explained Westword




What Are The Greenhouse Gas Emissions Of A Mini Grid Project And How Are They Calculated Mini Grids Support Toolkit Energy U S Agency For International Development




Ghg Emissions Environmental Reporting



Ghg Reduction Sustainability And Public Health Mndot
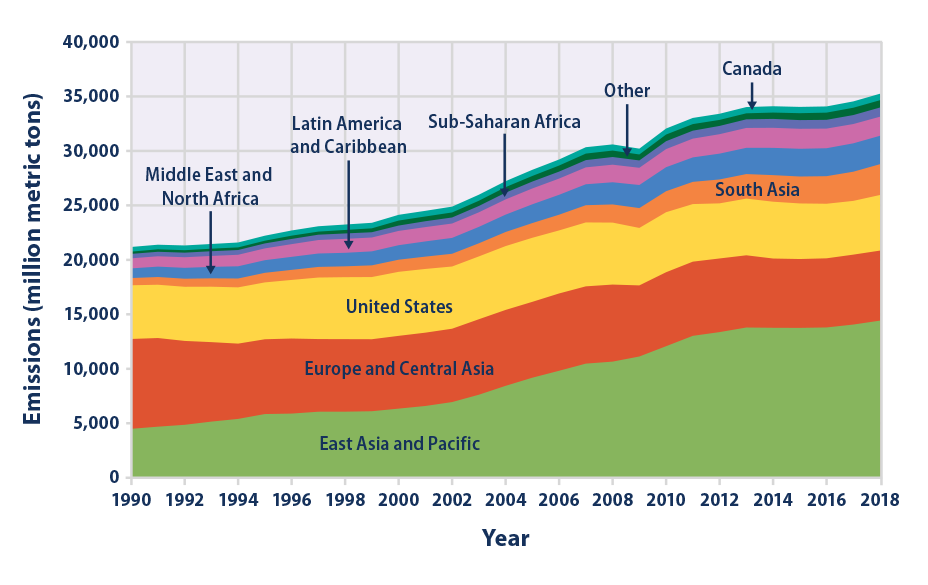



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa



Greenhouse Gases
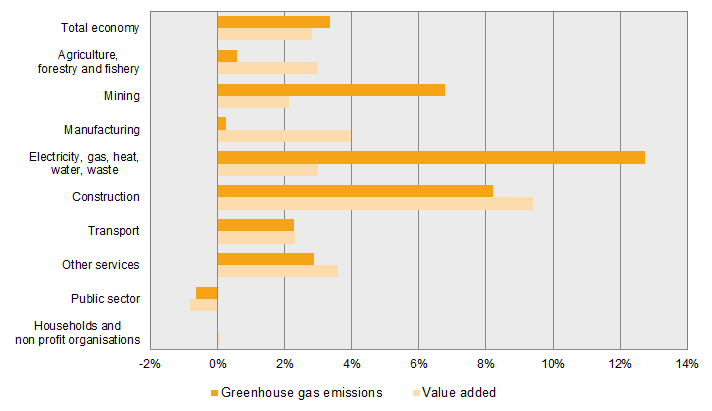



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Increased In First Quarter Of 18




Greenhouse Gas Emissions




What S Going On In This Graph Nov 19 The New York Times
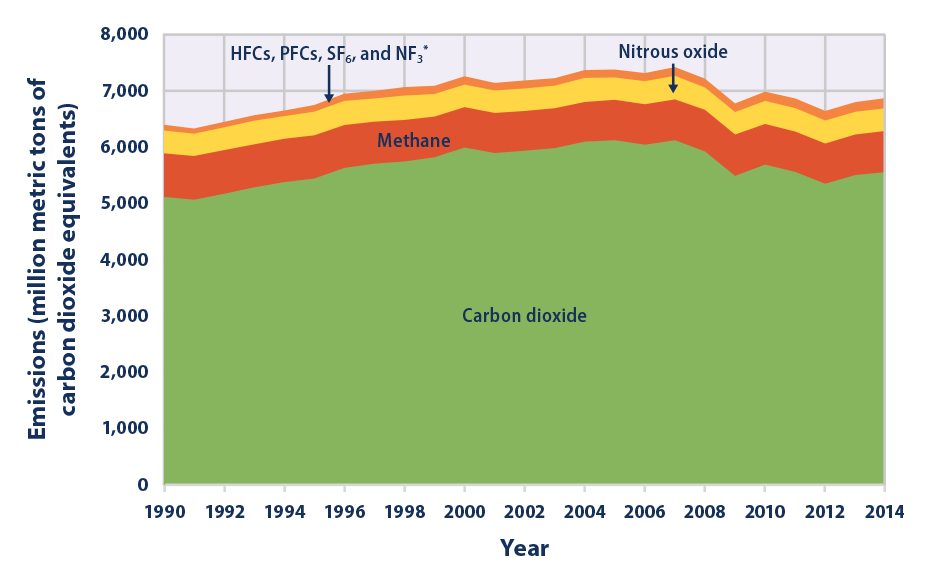



Climate Change Indicators U S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa
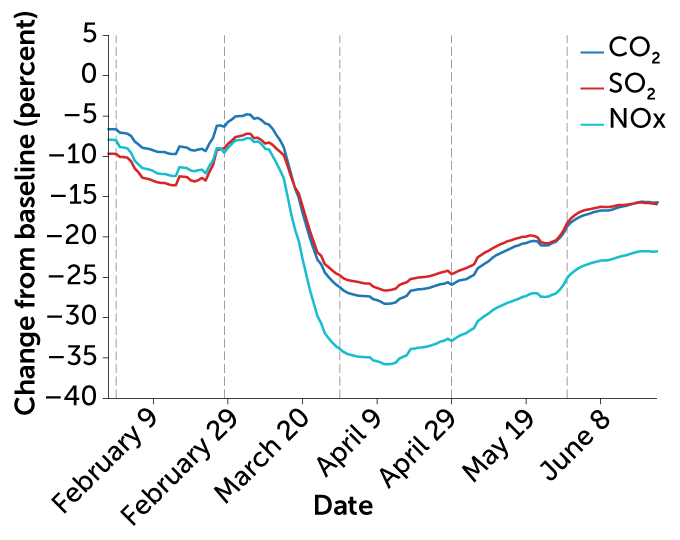



Covid 19 S Emissions Reductions Won T Impact Climate Change Science News
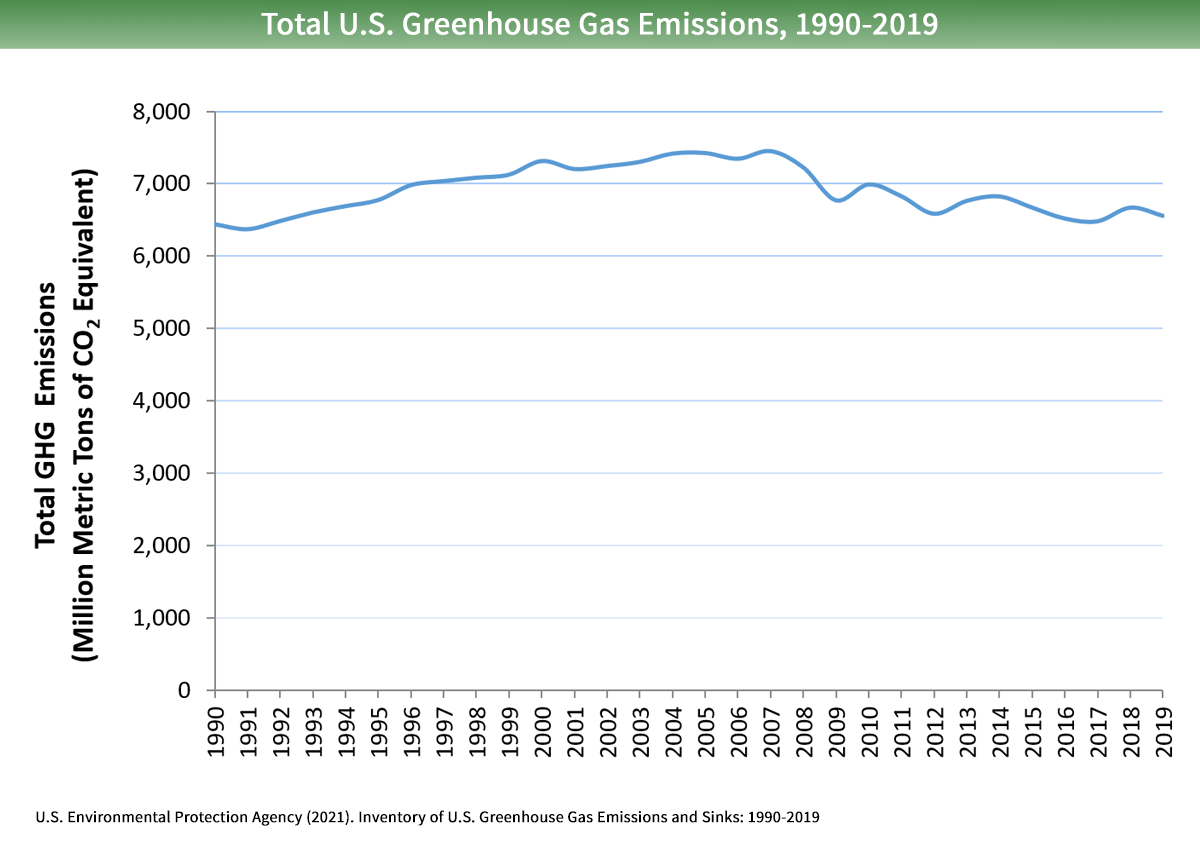



Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa
.png)



Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Waste Products Eurostat News Eurostat



Greenhouse Gases



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Germany S Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Energy Transition Targets Clean Energy Wire
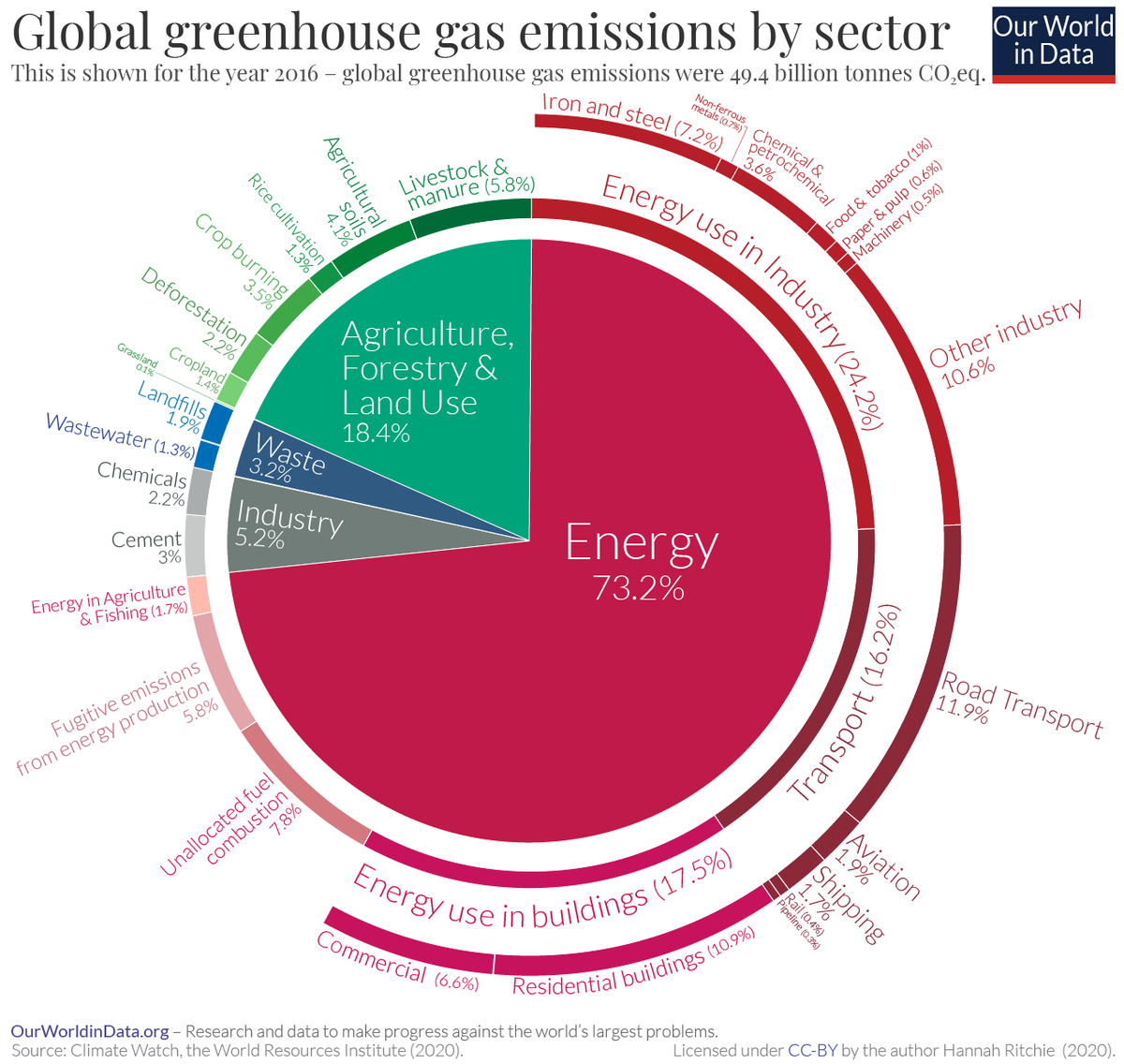



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
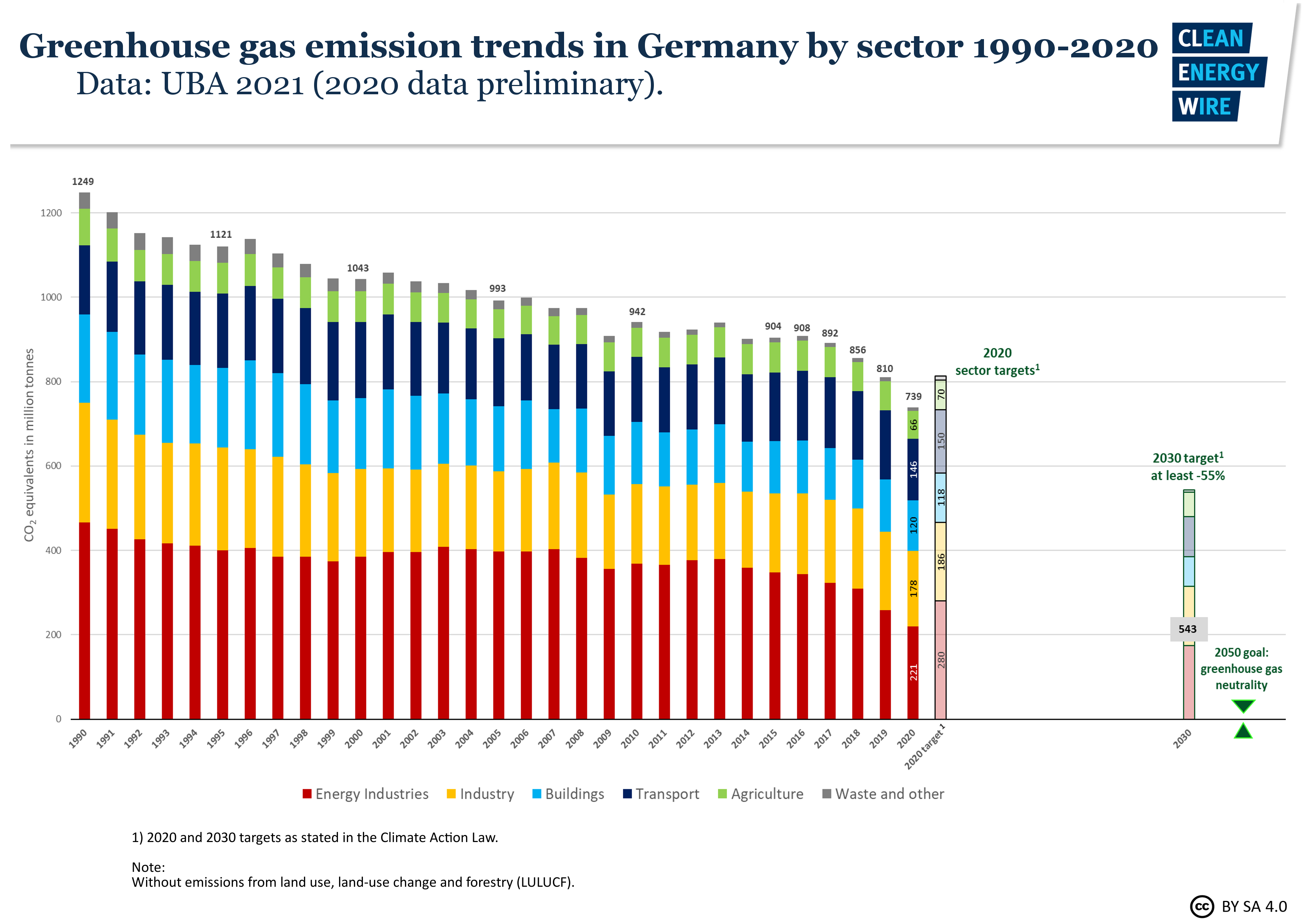



Germany Sees Record Greenhouse Gas Emission Fall Due To Pandemic Renewables Clean Energy Wire
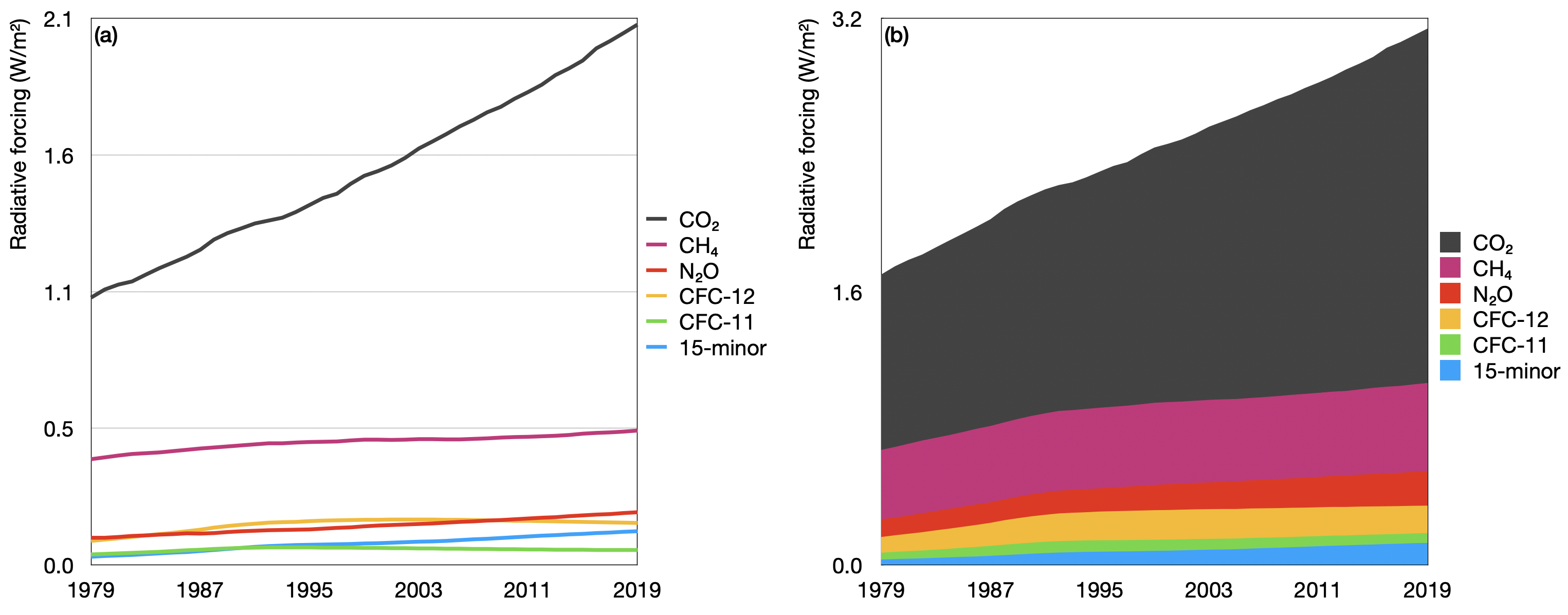



Greenhouse Gas Emissions




Graph Ireland S Share Of Greenhouse Gases From Agriculture Highest In Eu 17 April 16 Free




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions In The Unmitigated Reference Download Scientific Diagram
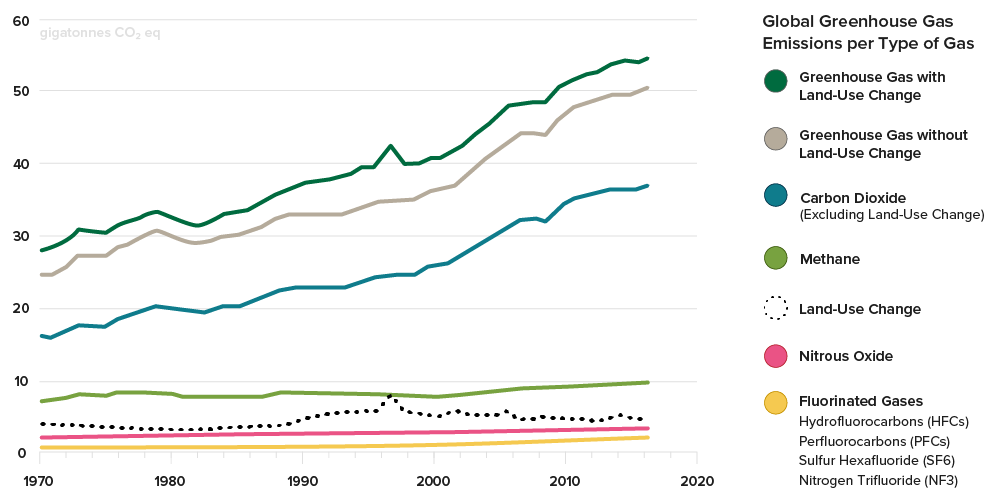



Carbon Emissions Forestry Carbon Credits The Arbor Day Foundation
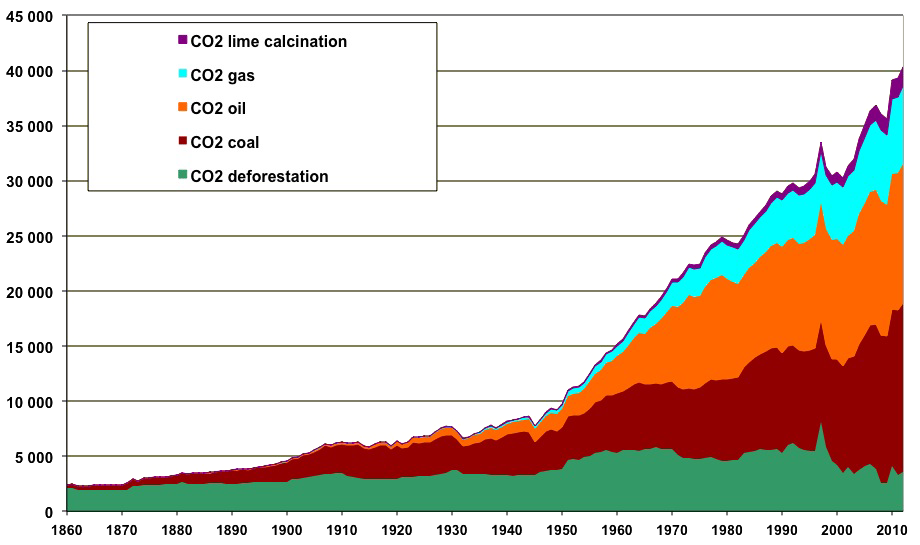



How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici
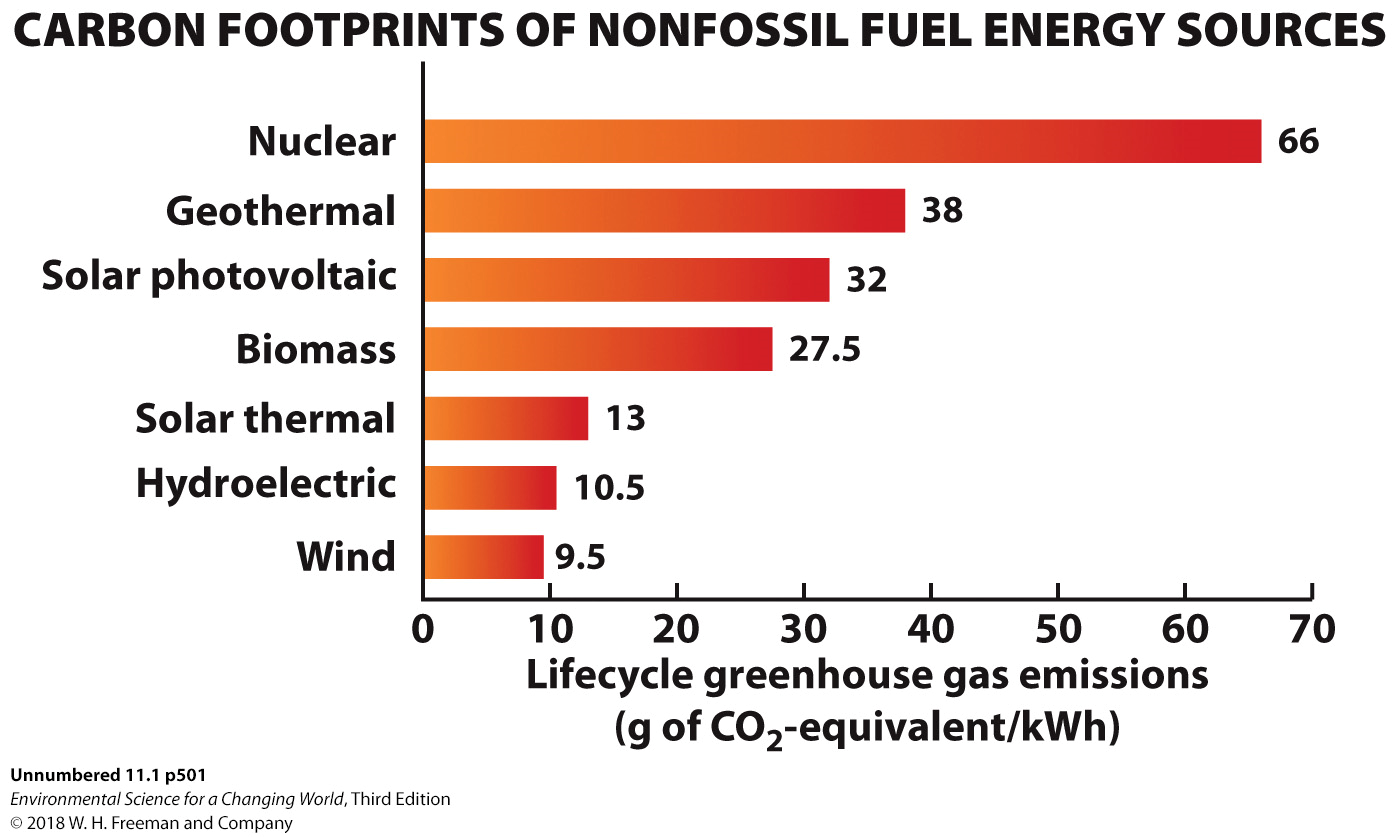



The Graph Illustrates The Lifecycle Greenhouse Gas Chegg Com
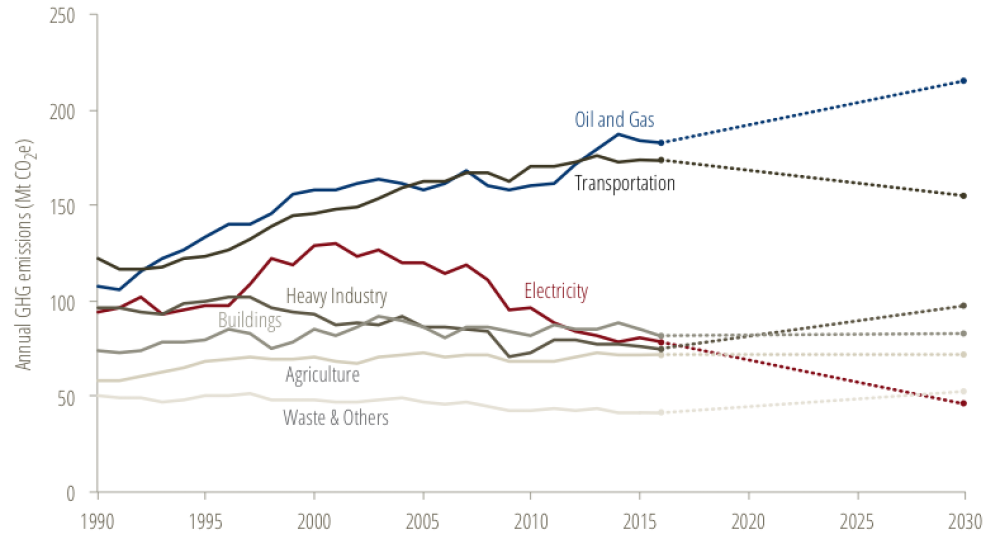



Three Takeaways From Canada S Latest Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Blog Posts Pembina Institute
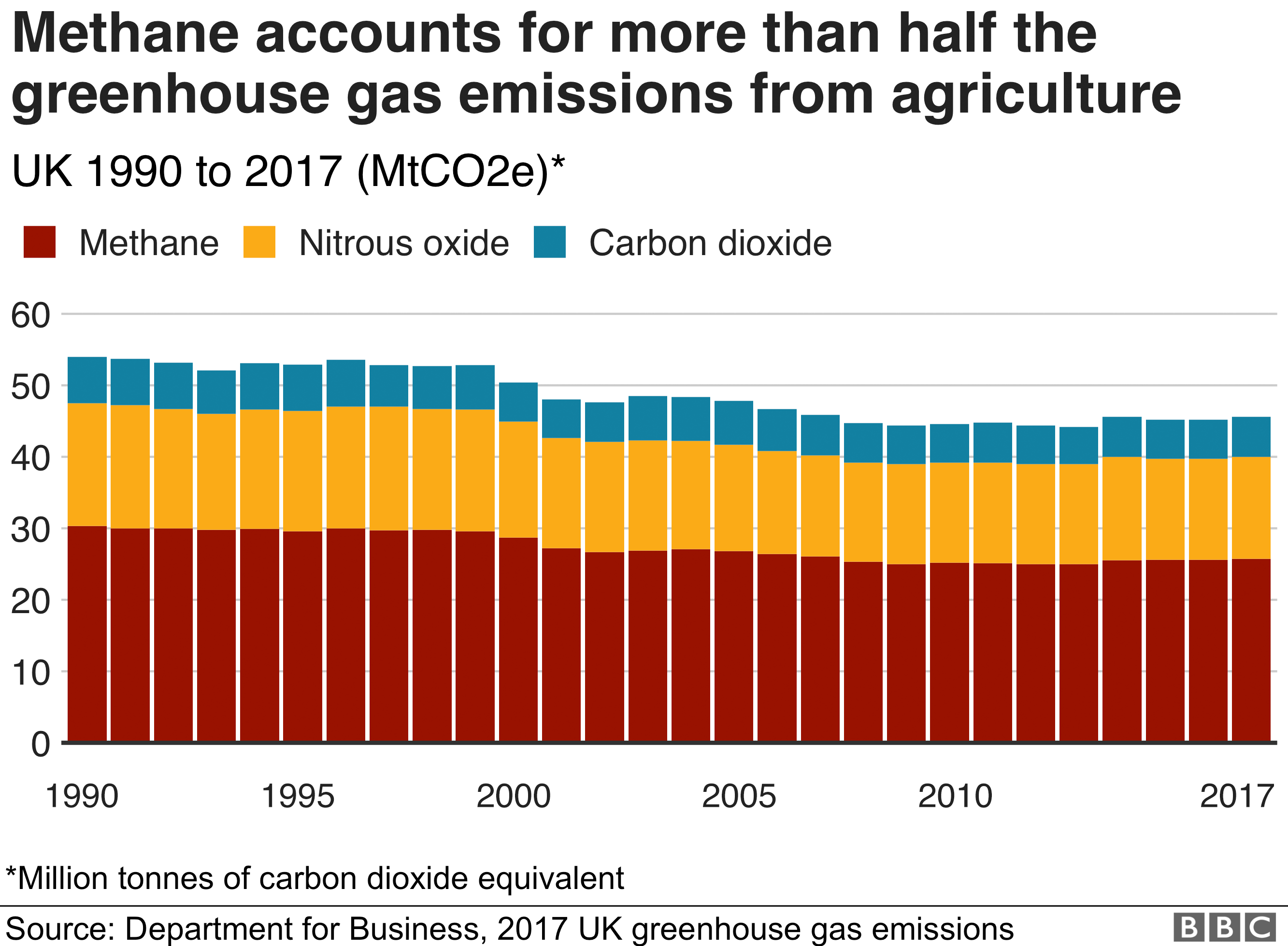



Five Ways Uk Farmers Are Tackling Climate Change c News



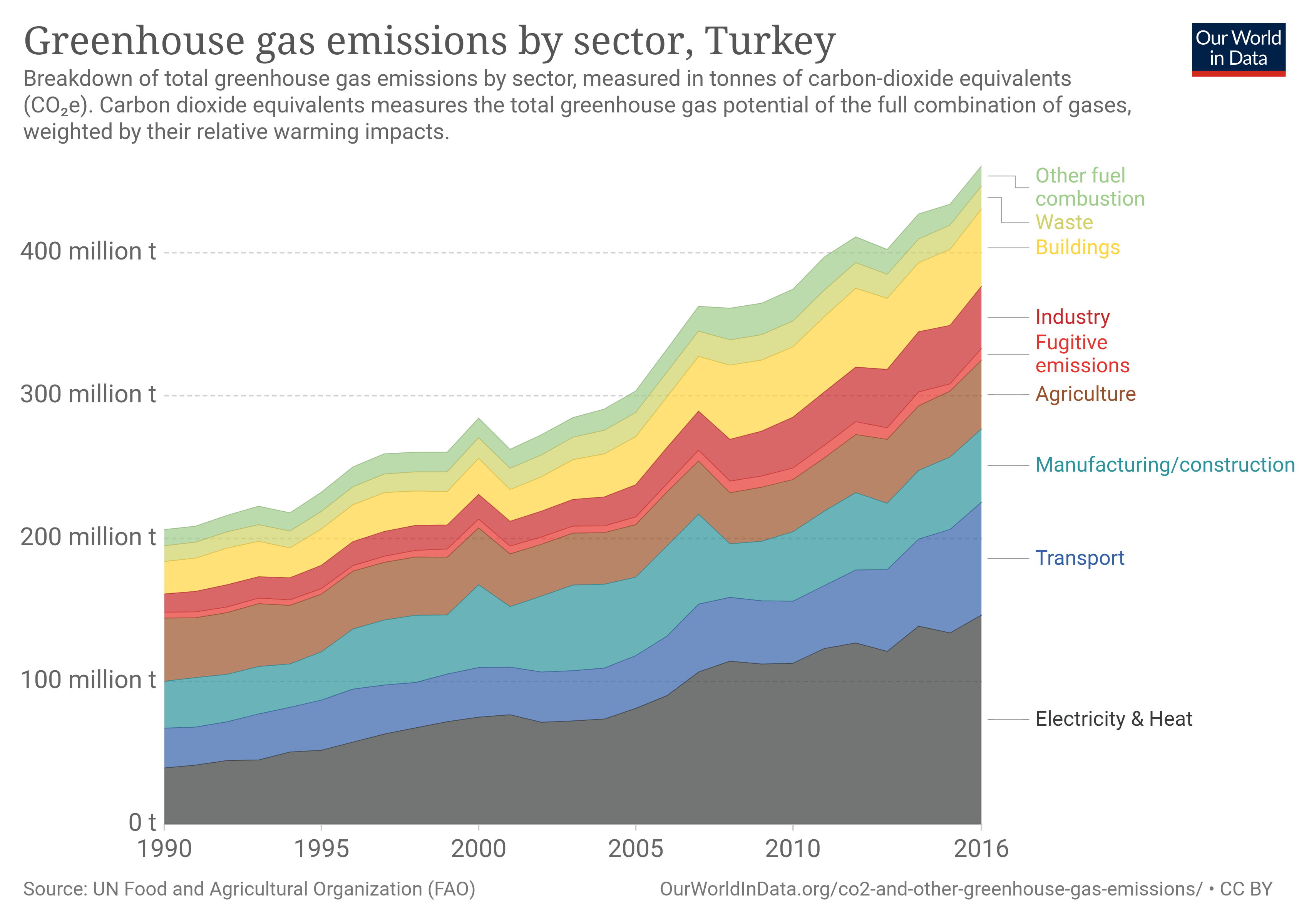
File Greenhouse Gas Emission And Absorption By Turkey Svg Wikimedia Commons




This Graph Shows How The Total Amount Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Has Been Increasing Around The World Greenhouse Gases Climate Change Greenhouse Gas Emissions




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




Changes Since The Industrial Revolution American Chemical Society



Q Tbn And9gcqob5akx 2xithdb3seiv5jyef5ryrbg3xvzguy4p57lypo5m0p Usqp Cau
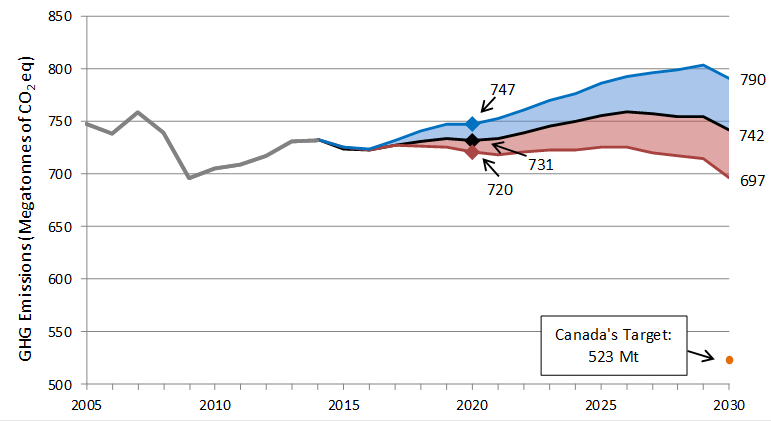



Modelling Of Greenhouse Gas Projections Canada Ca
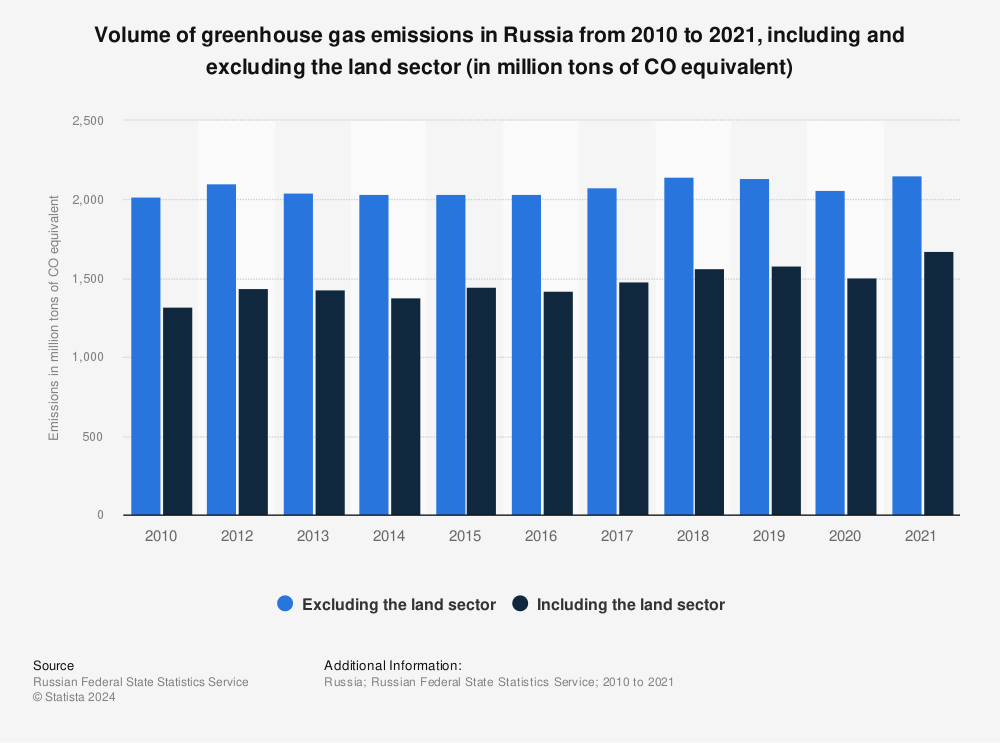



Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Russia Statista



10 Uconn Greenhouse Gas Inventory Office Of Sustainability
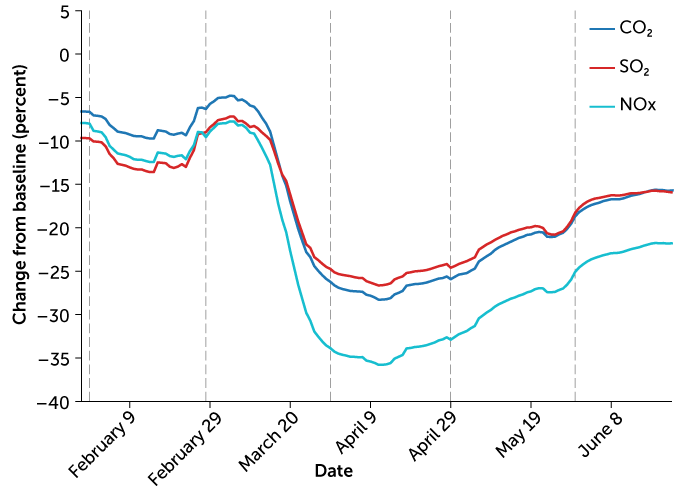



Covid 19 S Emissions Reductions Won T Impact Climate Change Science News
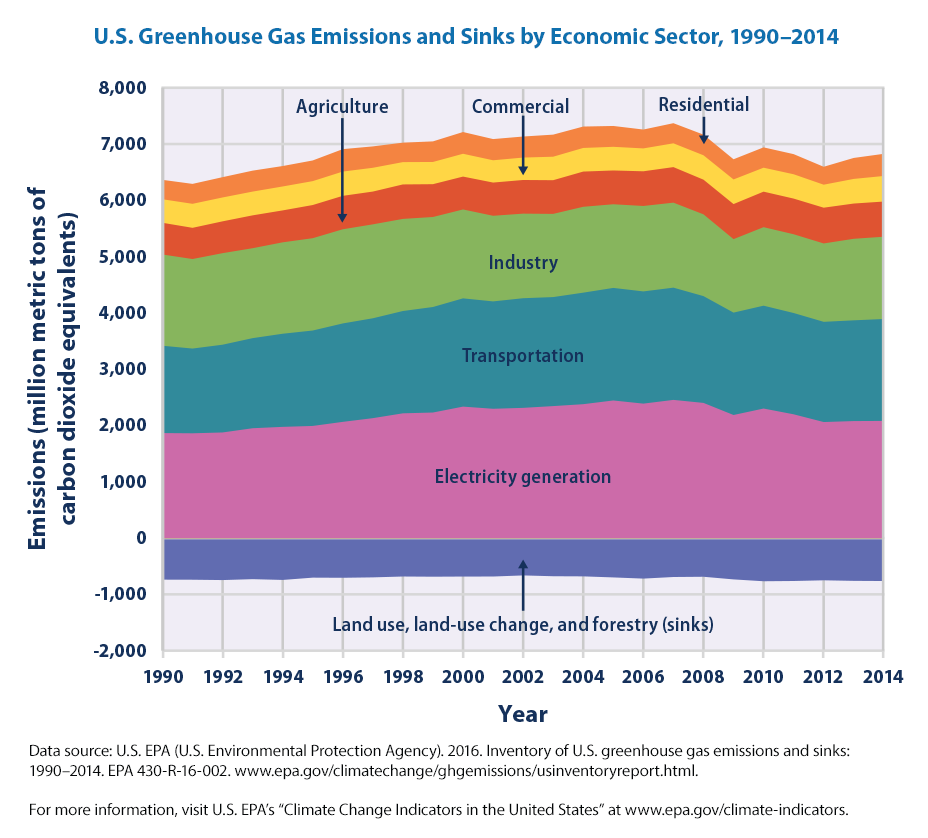



Climate Change Indicators U S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming




Assessment Of The Trends Of Greenhouse Gas Emission In Ethiopia Engdaw Geography Environment Sustainability




Graph Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Temperature Google Search Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse




U S Ghg Emissions At Lowest Level In Years Climate Central




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Food Type Per Capita By Diet And Download Scientific Diagram




52 Of World S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Just 25 Cities World Economic Forum



Q Tbn And9gcs3 Vn3xnwnq9ifctpyrsa2ofh2ymxfw2rxlcy7frr77uflqr Usqp Cau




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Per Capita And Per Unit Of Gdp In Purchasing Power Standards In 08 European Environment Agency




Assessment Of The Trends Of Greenhouse Gas Emission In Ethiopia Engdaw Geography Environment Sustainability



Greenhouse Gas Emissions By The United States Wikipedia
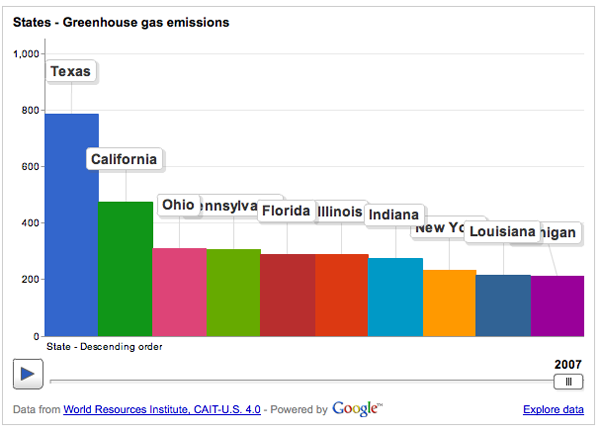



Greenhouse Gas Emissions By State Wri And Google Team Up Graphic Sociology



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data




Noaa S Greenhouse Gas Index Up 41 Percent Since 1990 Welcome To Noaa Research
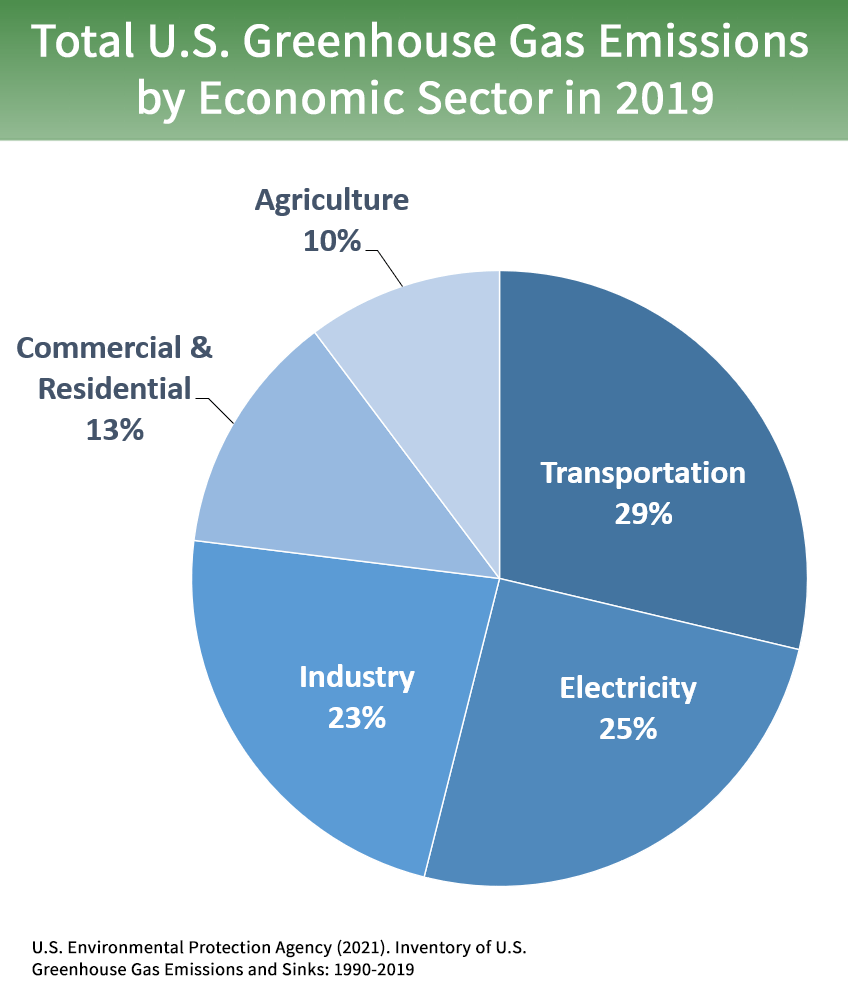



Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central




Graph Of The Day Noaa Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Aggi 1700 15 Desdemona Despair



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
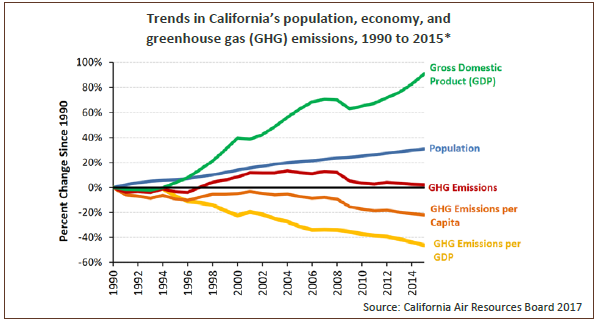



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Oehha




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Indicator Annual Greenhouse Gas Index 19 Indicator Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Gcis




File Annual Greenhouse Gas Index 1979 08 Epa 10 Indicator Of Radiative Forcing Png Wikimedia Commons




Boston S Latest Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Boston Climate Action Network




California Plans To Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions 40 By 30 Today In Energy U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Worldwide Greenhouse Gas Emissions From 1750 To 13 Data Source 16 Download Scientific Diagram




6 Graphs Explain The World S Top 10 Emitters World Economic Forum Greenhouse Gases World



Chart China Beats U S Europe In Combined Greenhouse Gases Statista
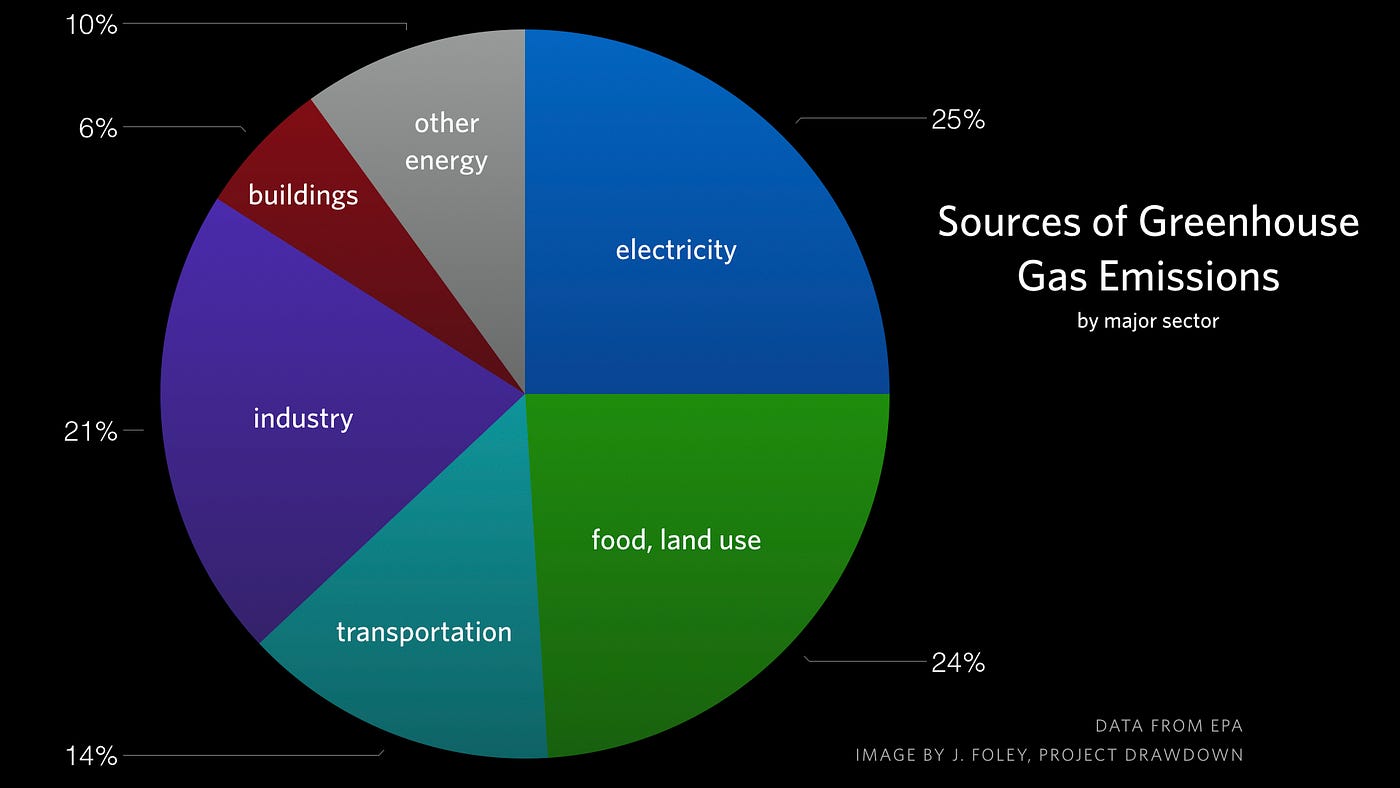



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org




Agriculture Sector Emissions Climate Change Greenhouse Gas Emissions Sources Of Greenhouse Gases Emissions
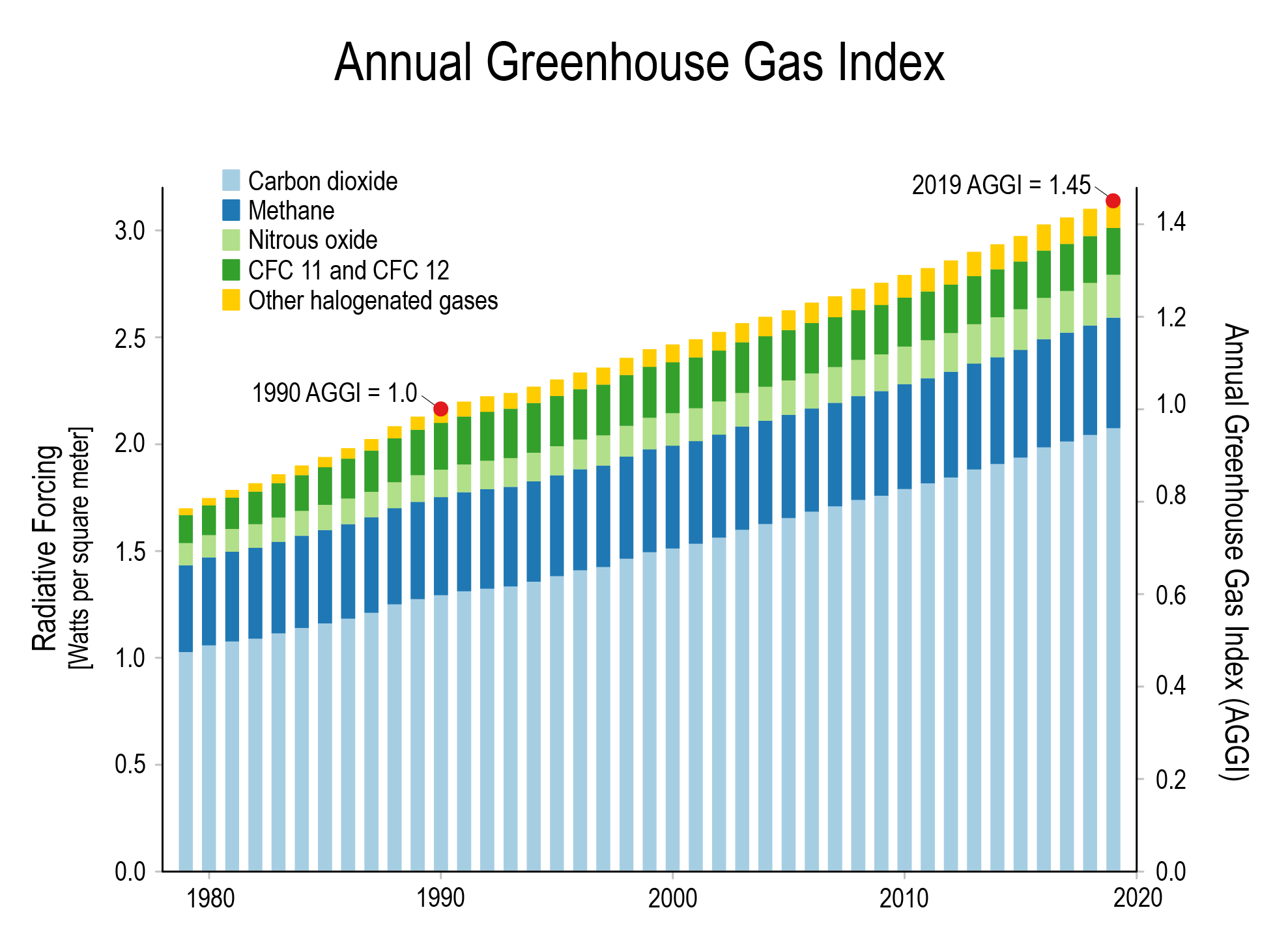



Climate Change International Ccs Knowledge Centre




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Plunged 17 Percent During Pandemic The Washington Post




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
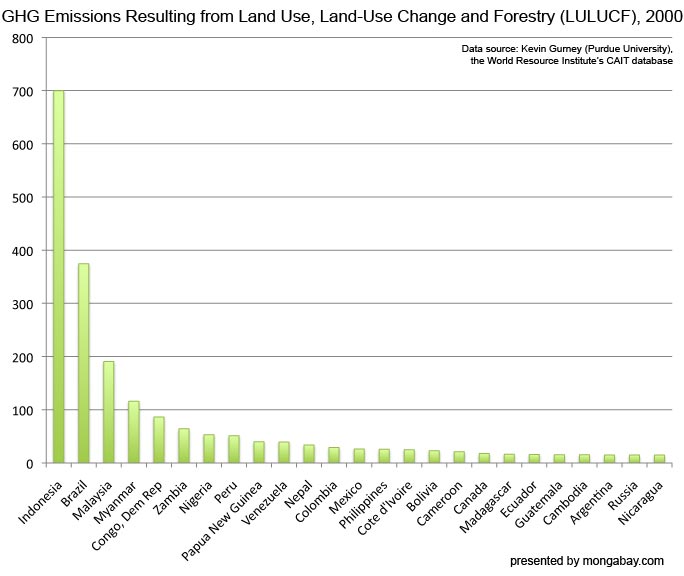



National Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Energy Use And Deforestation




1 4 Reduction Of Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emission Egee 439 Alternative Fuels From Biomass Sources




Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa




This Graph Shows The Increasing Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases In Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Gases Archives Darrin Qualman




Analysis Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions In The European Union Member States With The Use Of An Agglomeration Algorithm Sciencedirect



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿